You don't want to be the guy at the office who has to type everything in Microsoft Excel over and over again.
So there will come a time when you have to deal with all kinds of information stored in other types of files and bring it into Microsoft Excel. You can't run away from an ever-present text file. I bet you find some of them every day..
Here are some everyday examples:
Microsoft Excel gives you all the tools to connect to external data sources. Let's talk about delimited text files.
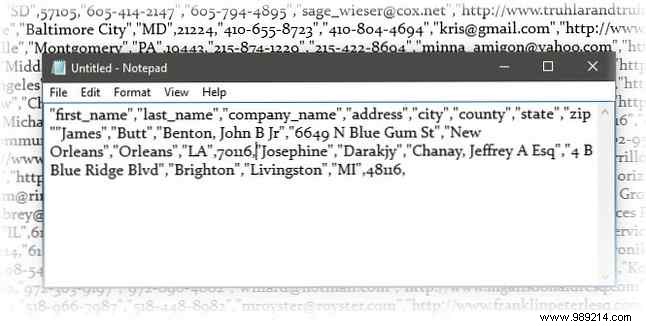
In this screenshot of a simple text file, names and addresses are separated by commas. This is a simple comma delimited text file . It's easy to create in any text editor.
But on its own, a whole series of such data would not be as useful in a text file if you had to prepare a list or a report. Putting it into an Excel spreadsheet will help you create a more professional document and perform more advanced operations on the information. For example, you can easily find duplicate addresses and remove them. You can then use the spreadsheet to create labels and mail merge. How to print mail merge labels in Microsoft Word and Excel. How to print mail merge labels in Microsoft Word and Excel. Still using copy and paste to create labels? Badges, or other mass personalized communications? Mail Merge, a simple Microsoft Office automation tool, will have you printing your labels in seconds. Read more.
The basic idea here is to import the information from a text file and divide the different pieces of information into separate columns, and name each column with an appropriate heading.
Let's look at the delimited text file in more detail...
Delimited text files are designed to export data from one program to another. There are three common types of files delimited by the way you separate (delimit) each value in the plain text file. Any character can be used to separate individual entries in a file.
For example:the pipe or a simple space. You will find that these three are the most common types of delimited separators between each text input.
As it's called, The Text Delimiter keeps each value separate from the next . Any value that follows the delimiter and precedes the next occurrence of the delimiter is imported as a value. Remember that the value between the assigned delimiter can have another delimiter character, but it requires a quote (") or an apostrophe (').
Confused? Not that much. Let's see how with an example:
In a text file with city and state names, there might be some values like “Albany, NY”. Microsoft Excel can read the comma (,) between the two words as a delimiter. Treat city and country names as a value and import them into a cell we have to use double quotes or an apostrophe as the text qualifier. If no character is specified as the text qualifier, "Albany, NY" is imported into two adjacent cells as Albany and NY.
In short, to preserve any value in a column as it is, you can enclose the value in quotes or an apostrophe. As we will see below, Microsoft Excel gives you complete control over the import process and a Preview panel to see the formatting of the data before filling the cells.
There are many online converters How to Convert Any File Format Online With Free Tools How to Convert Any File Format Online With Free Tools If you need to convert a file, this is the ultimate list of sites to turn to. Read More Zamzar and Convertio float to the top of the search page.
But you don't need to look for a converter online because Microsoft Excel has a native feature that does the job much better. Let's take a sample CSV file and walk through the steps to convert delimited text files to spreadsheets. The screenshot below shows a mix of comma separated values in a Notepad file.

Microsoft Excel can help turn this confusing mess into neat rows and columns. You can then go to work on it and turn it into a beautifully formatted report. Automatically format data in Excel spreadsheets with conditional formatting. Automatically format data in Excel spreadsheets with conditional formatting. worth. We show you how to use this for various daily tasks. Read More

There are two ways to bring data into an Excel 2016 spreadsheet from a CSV file. Start with the easy first.
Click on the File tab, then click Open .
Select the CSV file you want to open. Microsoft Excel automatically opens the text file and displays the data in a new workbook.
This is the most direct (and fastest) route to open a CSV file. Microsoft Excel uses default data format settings to read and import each column of data. But automatic import doesn't give you the flexibility you want. So let's look at the second way that uses a wizard.
The Text Import Wizard allows you to control the structure of the data you want to import. It starts automatically when you import text files (ie a file with a TXT extension). Open Microsoft Excel and browse to a text file. The three-step process helps you control the format of the data you want to import.
This is what the Text Import Wizard looks like in the first step.

But as seen above, the text import wizard does not start automatically for CSV files (ie a file with a .CSV extension). Open the Text Import Wizard manually and check the formatting of the rows and columns. To start the Text Import Wizard...
Go to the Data tab on the tape. In the Get external data group, select From text . In the Import text file In the dialog box, select the CSV text file you want to import. The Text Import Wizard is displayed with the options you can now configure.

The wizard will take you through three screens and help you adjust the data you're trying to get into the spreadsheet.
Select Delimited - When elements of the text file are separated by tabs, colons, semicolons, spaces, or other characters.
Select Fixed Width - When all the elements have the same length and are well structured in columns separated by spaces.
Sometimes the raw data may have a header row. For example:["first_name", "last_name", "company_name", "address", "city", "county" ].
Use Start import at row to select the row from where the import will start.
The File Source It can be left at its default value for most cases.
the Advance displays the values as they will appear when bounded in columns in the worksheet.
Click Next .
Choose the Delimiters for your file (comma, in our case). For some other character, check Other and enter the character in the small field. The Data Preview The window gives you a glimpse of the data in columns.

Select the Treat consecutive delimiters as one check the box if your data contains a delimiter of more than one character between data fields or if your data contains multiple custom delimiters. For example, this helps you handle files that may have an extra space before or after another delimiter. It may help to identify the space as another delimiter and check this box.
Use the Text qualifier dropdown to select the character that encloses values in your text file. We discussed earlier how a text qualifier can help you import some values into a cell instead of separate values.
Use the Data preview Window to check the appearance. Click Next .
The wizard screen changes when importing fixed-width data. The Data Preview The window can help you set the column widths. Use the top bar of the window to set a column break represented by a vertical line. Drag a column break to increase or decrease the width. Double-click a column break to remove it.

In a fixed-width file, no delimiters are used to separate the values in the file. The data is arranged in rows and columns, with one entry per row. Each column has a fixed width, specified in characters, that determines the maximum amount of data it can hold.
The Preview windows become more important on this screen because you can adjust the format of the data going into each field with the Column Data Format . By default, Microsoft Excel imports data in the General format. Select the column in the preview window and set the appropriate format.
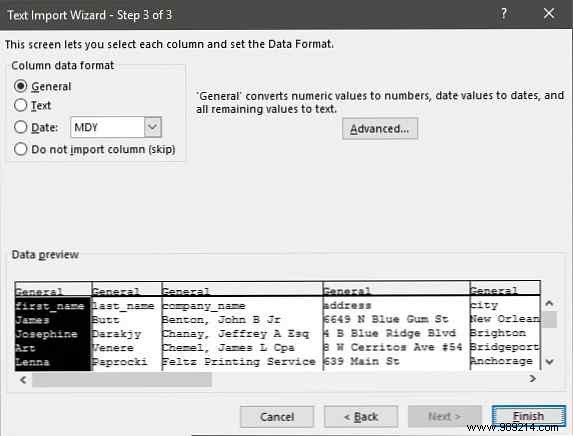
For example, you can select ...
Use the Advanced Button to specify the type of decimal and thousands separators for numeric data. For example, if you want to display 100,000 as 1,00,000. Excel displays numbers according to the format set in your computer's regional settings.
Click Finish . One final Import data the dialog box appears.

Don't worry too much now. It gives you a few options to insert the data into the spreadsheet or create a connection to an external database. The default setting is to insert the text-delimited values as a table in the current worksheet.
Some practice proficiency in Microsoft Excel Do you need to learn Excel? 10 experts will teach you for free! Do you need to learn Excel? 10 experts will teach you for free! Learning to use the more advanced features of Excel can be difficult. To make it a little easier, we've tracked down the best Excel gurus that can help you master Microsoft Excel. Read More You can import or export up to 1,048,576 rows and 16,384 columns. Don't let big data scare you. If the fear of spreadsheets is still getting to you, check out these tips for learning Excel 8 Tips for Learning Excel Quickly 8 Tips for Learning Excel Quickly Not as comfortable with Excel as you'd like? Get started with simple tips for adding formulas and managing data. Follow this guide and you'll be up to speed in no time. Read faster.
So, w What kind of problems do you face when exporting delimited text files? Let's fix it for each other in the comments.