When you think about Excel (our top Excel tips 8 Tips to Learn Excel Fast 8 Tips to Learn Excel Fast Not as comfortable with Excel as you'd like? Start with simple tips for adding formulas and managing data. Follow this guide, and you'll be up to speed in no time. Read More But it also adds text to spreadsheets, such as headings, descriptions, or people's names.
Today we will cover several ways to work with text in Excel spreadsheets. We discussed several different functions for working with text. Whenever you use a function, always start with an equal sign (=).
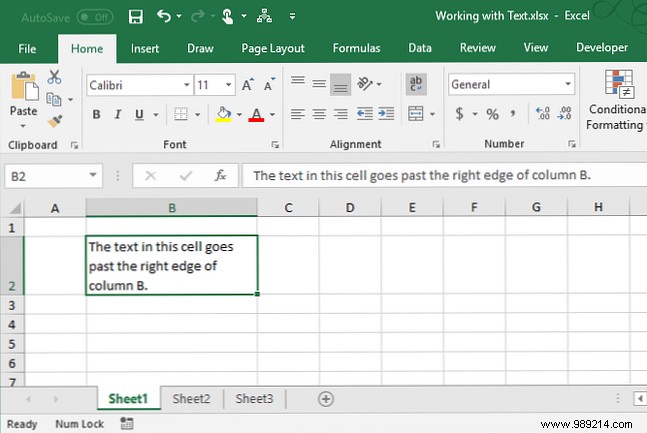
When you enter text into a cell that is wider than the cell, the text extends past the right border of the cell by default. But it's easy to make the text fit the width of the column. Text wrapping automatically wraps when the cell width changes.
To make text wrap in a cell, select the cell and click Wrap text button on the Alignment House section tab.

The text wraps in the cell and the row height automatically adjusts to fit the text.
If the row height does not adjust automatically, the row can be set to a specific height.
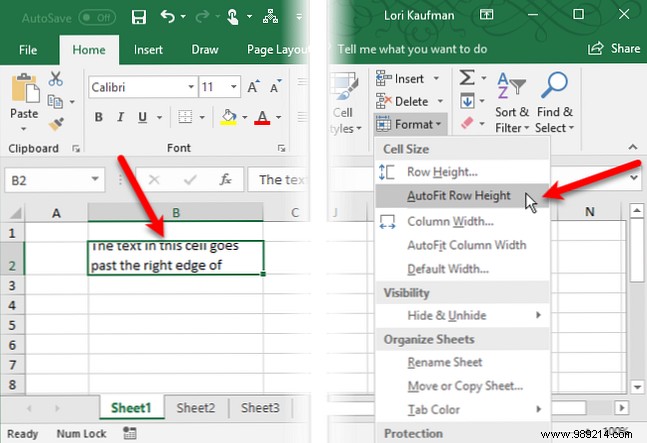
To automatically fit the row height to the text, select the cell. Then click Format in the Cells section on the House tab and select AutoFit Row Height .
If you want to keep the row at a specific height, you can change it to make sure the wrapped text fits. Select Row Height from the Format menu. Then enter a height for the row in the Row Height dialog and click OK .
You can also drag the bottom border of the row down until all lines of text fit in the cell.
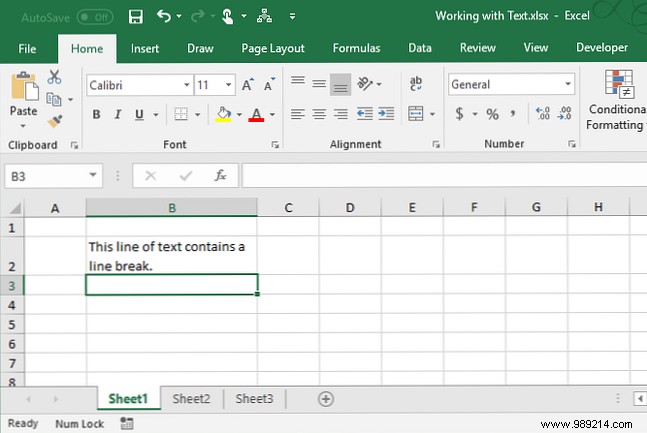
If the text in a cell goes past the right border, you can also insert a line break to make the text wrap completely.
Double click the cell to edit the text or press F2 . Click the mouse at the point in the text where you want to insert a line break. Then press Alt + Enter .

The row height adjusts to fit the text if the Format set to AutoFit row height in the Cells House section tab.
If you want to know how many cells in a range in your worksheet contain text (not numbers, errors, formulas, or blank cells), you can use the COUNTIF function Mini Excel Tutorial:Using Advanced Counting and Adding Functions in Excel Mini Excel Tutorial :Using Advanced Counting and Adding Functions in Excel Counting and adding formulas can seem mundane compared to more advanced Excel formulas. But they can help you save a lot of time when you need to gather information about the data in your spreadsheet. Read more.
The generic form of the COUNTIF function to count any number of characters in text is:
= COUNTIF (rango de celda, "*")The cell range represents any range of cells like B2:B9. The asterisk between the quotes is a wildcard character that represents any matching number of text characters. There are a few things to note about what counts as text characters:
For example, to count the number of cells that contain text in cell range A2:G9 in the following worksheet, we enter “=COUNTIF(“. Then, to enter the cell range, we select the cells we want to include in the count..
The COUNTIF function is not case sensitive.
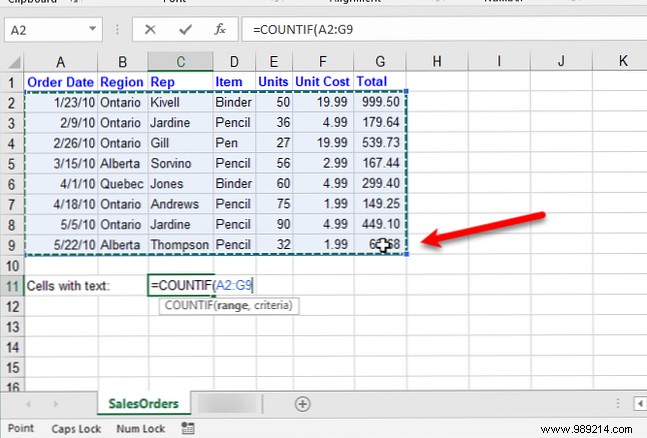
Next, we enclose a comma (,) and the wildcard character (*) in double quotes.
press Enter to complete the input of the function and see the result in the cell.
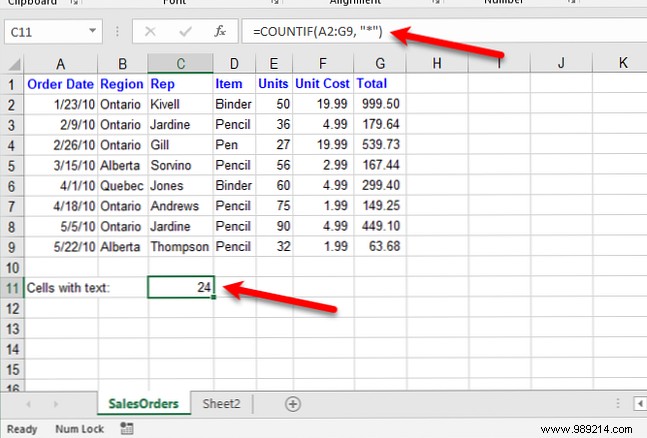
You can also use the COUNTIF function to count how many cells contain specific text characters.
The generic function to count the occurrences of text characters in a specific string is:
= COUNTIF (cellrange, "txt")As in the previous section, cell range represents any range of cells like B2:B9. We put the string of text characters that we want to find between double quotes.
For example, to count the number of cells containing "Pencil" in cell range A2:G9 in the following worksheet, we enter the following function:
= COUNTIF (A2: G9, "Lápiz")This finds all cells that contain only the word "Pen" with no other text in the cell. Because the COUNTIF function is not case sensitive, it will find all cells that contain "Pen" or "pen".
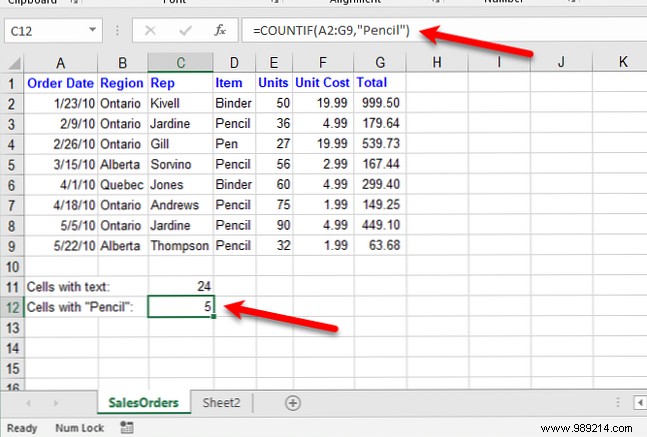
The COUNTIFS function allows you to count cells with text but exclude Cells with specific text characters..
For example, we use COUNTRIES as follows to find all cells that contain any text except for "Pencil".
= PAÍSES (A2: G9, "*", A2: G9, "<> Lápiz")For the COUNTRIES function, you first need to give it the range and text you want to find. Then give it the same range again and the text you want to exclude. The "<>" is used to exclude any text that follows.
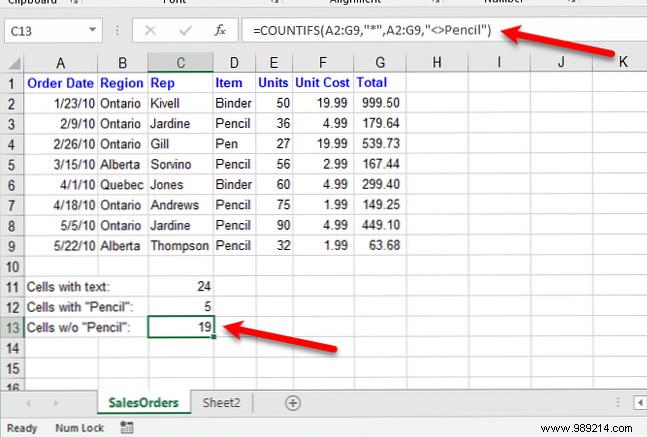
By using the COUNTIF or COUNTIFS function, you can add an asterisk to one or both sides of the string to find cells that contain that string surrounded by any number of text characters (or none).
For example, to find all cells that contain the letter. “j”, We use the following function:
= COUNTIF (A2: G9, "* j *")Again, because the COUNTIF function is not case sensitive, cells containing "j" or "J" will be counted.

If you have a lot of cells that contain numbers stored as text, there are a few ways you can convert the text to numbers.
You can tell if a number is formatted as text when it is left-aligned in the cell instead of right-aligned. Also, if a number has been forcibly formatted as text using an apostrophe (') at the beginning, there will be a green triangle in the upper left corner of the cell.
To convert text to numbers you can use the Convert to number option, the Text to Columns feature, or Paste Special . We discuss each of these methods in our article on how to extract numbers and text in Excel.
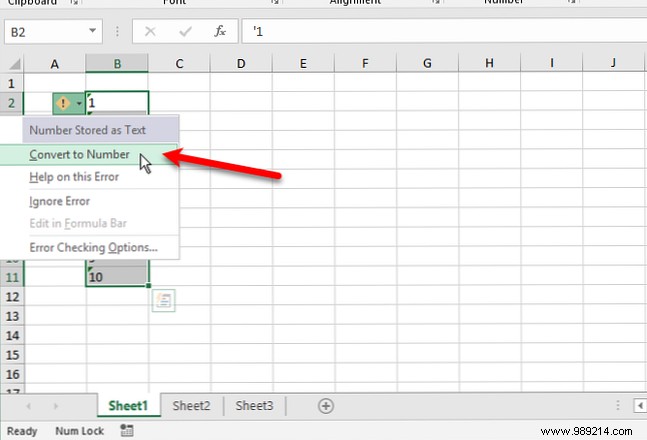
There may be times when you want to store numbers as text. Maybe you're performing an action on a range of cells and there are certain cells that you don't want to read as numbers, even though they are.
Typing an apostrophe (') at the beginning of a number converts it to text. But if you have many cells with numbers that you want to convert to text, you can use the TEXT function.
For example, we want to convert the numbers in column B shown below to text. We write the following function in the cell to the right of the first number.
= TEXTO (B2, "0")You give the function the cell reference for the number to convert and then the number format you want. We're just converting to a number with no special formatting (not currency or a date, for example). So we use “0” (zero).
Use AutoFill How to use Excel Flash Fill and Auto Fill to automate data entry How to use Excel Flash Fill and Auto Fill to automate data entry When you regularly create and fill Excel spreadsheets with data, you should know about autofill and Flash Fill. Let us show you what these features do and how they can help you. Read More Numbers are converted to text and aligned to the left.
You can copy and paste the converted values to the original column. Select the cells that contain the TEXT function and press Ctrl + C to copy them. Select the first cell in the original column. About the House tab, click the arrow on the Paste button and go to Paste Special> Values .
You can find examples of the different text formats available for use in the TEXT function on the Microsoft support site.

Have you ever received a workbook from someone else where they entered dates as text, as numbers, or in an unrecognizable format as dates? You can convert text to dates using the DATE function.
Here is the generic format of the DATE function:
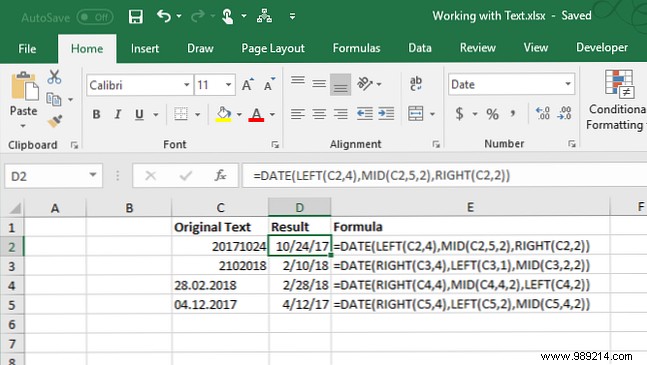
= FECHA (año, mes, día)For the year, month, and day, we are going to use the LEFT, MID, and RIGHT string functions to extract the appropriate parts of the text or number that we want to convert. We will explain the four examples in the image below.
To convert “20171024” in cell C2 to a date, we use the LEFT function to extract the first four characters of the year (2017). Next, we use the MID function to extract the two characters starting in the fifth position as month (10). Finally, we use the RIGHT function to extract the last two characters as the day (24).
= FECHA (IZQUIERDA (C2,4), MID (C2,5,2), DERECHA (C2,2))The following example, "2102018" in cell C3, is in a different order. We still use the string functions but in a different order. We use the RIGHT function to extract the last four characters of the year (2018). The month is just a digit in this case, so we use the LEFT function to extract the first character as the month (2). Finally, we use the MID function to extract the two characters that start in the second position as the day (10).
= FECHA (DERECHA (C3,4), IZQUIERDA (C3,1), MID (C3,2,2))The dates in cells C4 and C5 look like normal dates, but Excel doesn't recognize them as dates. In cell C4, the format is day, month, year. So we use the RIGHT, MIDDLE and LEFT functions as follows:
= FECHA (DERECHA (C4,4), MEDIA (C4,4,2), IZQUIERDA (C4,2))In cell C5, the format is month, day, and year, using two zeros versus a single-digit month. So we use the RIGHT, LEFT and MIDDLE functions as follows:
= FECHA (DERECHA (C5,4), IZQUIERDA (C5,2), MID (C5,4,2))
Using the DATE function may seem like as much work as rewriting the text as dates. But it's very likely that the same format was used throughout your workbook if one person worked on it.
In that case, you can copy and paste the function and the cell references will snap to the correct cells. If they don't, just enter the correct cell references. You can highlight a cell reference in a function and then select the cell in which you want to enter that reference.
If you have a large amount of data in a worksheet and you need to combine text from multiple cells, there is an easy way to do it. You don't have to retype all that text.
For example, we have a worksheet that contains employee names and their contact information, as shown below. We want to separate the First Name and Last name and then combine them into one Full Name column. We can also create an Email Address Automatically combining the first and last name..
To do this, we use the CONCATENATE function 16 Excel formulas that will help you solve real life problems. 16 Excel formulas to help you solve real life problems. The right tool is half the job. Excel can solve calculations and process data faster than your calculator can. We show you the key Excel formulas and show you how to use them. Read more . A "concatenate" simply means "combine" or "join." This function allows you to combine text from different cells into one cell. You can also add any other text to the text in other cells.
To combine the Last Name and First name in a row in the Full name On the column, we use the CONCATENATE function as follows:
= CONCATENADO (B2, "", A2)Give the CONCATENATE function the text to combine in the order you want it to be combined. So we gave the function the First Name (B2), a space between double quotes (” “), then the LastName (A2).
We can also build the email address in the same way. We use the First Name (B2), the Surname (A2), and then the rest of the email address (@ email.com) in double quotes.
= CONCATENADO (B2, A2, "@ email.com")Always enclose any specific text in double quotes, but don't put quotes around cell references.

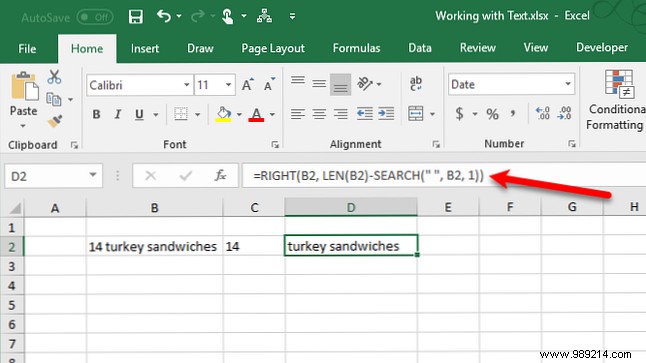
Do you have some cells with mixed format content that you want to separate? For example, if you have a cell that contains "14 turkey sandwiches," you can separate that into the number (14) and the text (turkey sandwiches). That way, you can use the number in functions and formulas.
To get the number of “14 turkey sandwiches”, we use the string function LEFT.
= IZQUIERDA (B2, BUSCAR ("", B2, 1))First, we give the function the cell reference for the text from which we want to extract the number (B2). Next, we use the SEARCH function to find the first space after the first character in the string.
To get the text out of “14 turkey sandwiches”, we use the RIGHT string function.
= DERECHA (B2, LEN (B2) -SEARCH ("", B2, 1))First, we give the RIGHT function the cell reference we want to extract the text from (B2). Next, we use the LEN and SEARCH functions to determine how many characters on the right we want to get. We are subtracting the number of characters from the first space after the first character of the string to the end of the string from the total length of the string.
Obtenga más detalles sobre la separación de texto en varias celdas en nuestro artículo sobre cómo extraer texto o números de celdas de formato mixto.
A veces, la hoja de cálculo en la que está trabajando tendrá demasiado texto. Esto te ayudará a simplificarlo..
Puede encontrar más detalles sobre las funciones que discutimos aquí en nuestro artículo sobre operaciones de texto Ahorro de tiempo con operaciones de texto en Excel Ahorro de tiempo con operaciones de texto en Excel Excel puede hacer magia con los números y puede manejar los caracteres igualmente bien. Este manual muestra cómo analizar, convertir, reemplazar y editar texto en hojas de cálculo. Estos fundamentos te permitirán realizar transformaciones complejas. Lea más, así como información sobre algunas funciones adicionales relacionadas que no mencionamos aquí.